Servlet基础
本文最后更新于:2020年12月24日 下午
一、Servlet概述
1)什么是servlet
- Servlet 是运行在服务器上的一个 java 小程序,它可以接收客户端发送过来的请求,并响应数据给客户端。
- Servlet 程序、Filter 过滤器和Listener 监听器并称为JavaWeb的三大组件
2)HelloWorld
编写类实现Servlet接口,在其中要实现service方法,处理请求并响应数据
public class HelloServlet implements Servlet { /** * service 方法是专门用来 处理请求和响应的 */ @Override public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("Hello Servlet 被访问了"); } }配置web.xml文件
<servlet></servlet>标签 给 tomcat服务器 配置Servlet程序,其中servlet-name一般采用类名,servlet-class为全类名<servlet-mapping>标签 将访问地址和Servlet程序建立关联,其中url-pattern为访问地址(不要忘了前面的斜杠),servlet-name即 将当前配置的地址给哪个Servlet程序
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app
3)url地址到Servlet程序的访问
4)Servlet的生命周期
- 执行构造器方法 -→ 执行初始化方法 -→ 执行service方法 -→ 执行destroy方法
- 构造方法和初始化仅执行一次,service方法每次访问时都会调用
- 在web工程停止时,才会调用destroy方法
5)Get请求和Post请求
public class HelloServlet implements Servlet {
/**
* service 方法是专门用来处理请求和响应的
*/
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("3 service === Hello Servlet 被访问了");
// 类型转换(因为它有getMethod()方法)
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
// 获取请求的方式
String method = httpServletRequest.getMethod();
if ("GET".equals(method)) {
doGet();
} else if ("POST".equals(method)) {
doPost();
}
}
/**
* 做get 请求的操作
*/
public void doGet(){
System.out.println("get 请求");
System.out.println("get 请求");
}
/**
* 做post 请求的操作
*/
public void doPost(){
System.out.println("post 请求");
System.out.println("post 请求");
}
}6)通过继承HttpServlet实现Servlet程序
编写一个类继承HttpServlet类,并重写doGet方法和doPost方法
public class HelloServlet2 extends HttpServlet { // 处理get请求 @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException { System.out.println("HelloServlet2 的doGet 方法"); } // 处理post请求 @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException { System.out.println("HelloServlet2 的doPost 方法"); } }在web.xml中配置Servlet程序的访问地址
<servlet> <servlet-name>HelloServlet2</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.HelloServlet2</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>HelloServlet2</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello2</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
7)IDEA创建Servlet程序
8)Servlet类的继承体系

二、ServletConfig类
ServletConfig类,即Servlet的配置类。
- 通过
servletConfig.getServletName()获取Servlet 程序的别名servlet-name 的值 - 通过
servletConfig.getInitParameter("username")获取初始化参数init-param - 通过
servletConfig.getServletContext()获取ServletContext 对象
HelloServelet 中的代码:
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
super.init(servletConfig) // 重写init方法时必须调用父类的init方法
System.out.println("2 init 初始化方法");
// 1、可以获取Servlet 程序的别名servlet-name 的值
System.out.println("程序的别名是:" + servletConfig.getServletName());
// 2、获取初始化参数init-param
System.out.println("值是;" + servletConfig.getInitParameter("username"));
System.out.println("url的值是;" + servletConfig.getInitParameter("url"));
// 3、获取ServletContext 对象
System.out.println(servletConfig.getServletContext());
}web.xml中的配置:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>username</param-name>
<param-value>root</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>url</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>三、ServletContext类
1)概念
- ServletContext是一个接口,它表示Servlet 上下文对象
- 一个web 工程,只有一个ServletContext 对象实例。
- ServletContext 对象是一个域对象。(这里的域指的是存取数据的操作范围,整个web工程)
- ServletContext 是在web工程部署启动的时候创建,工程停止时销毁。
2)作用
context.getInitParameter("username"):获取web.xml中配置的上下文参数context-paramcontext.getContextPath():获取当前的工程路径,格式:/工程路径context.getRealPath("/css"):获取工程部署后在服务器硬盘上的绝对路径
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 创建ServletContext对象
ServletContext context = getServletConfig().getServletContext();
// 1、获取web.xml 中配置的上下文参数context-param
String username = context.getInitParameter("username");
System.out.println("context-param 参数username 的值是:" + username);
System.out.println("context-param 参数password 的值是:" +
context.getInitParameter("password"));
// 2、获取当前的工程路径,格式: /工程路径
System.out.println( "当前工程路径:" + context.getContextPath() );
// 3、获取工程部署后在服务器硬盘上的绝对路径
/**
* /斜杠被服务器解析地址为:http://ip:port/工程名/ 映射到IDEA 代码的web 目录
*/
System.out.println("工程部署的路径是:" + context.getRealPath("/"));
System.out.println("工程下css 目录的绝对路径是:" + context.getRealPath("/css"));
System.out.println("工程下imgs 目录1.jpg 的绝对路径是:" + context.getRealPath("/imgs/1.jpg"));
}- 像Map一样存取数据
setAttribute():存数据、getAttribute():取数据、removeAttribute():移除数据
public class ContextServlet1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取ServletContext 对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
System.out.println(context);
System.out.println("保存之前: Context1——key1:"+ context.getAttribute("key1"));
context.setAttribute("key1", "value1");
System.out.println("Context1——key1 的值是:"+ context.getAttribute("key1"));
}
}
public class ContextServlet1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException,IOException {
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
System.out.println(context);
System.out.println("Context2——key1 的值是:"+ context.getAttribute("key1"));
}
}四、HTTP协议
1)概述
HTTP协议即超文本传输协议,也就是客户端和服务器之间通信时需要遵守的规则。
客户端 —> 服务器:请求
服务器 —> 客户端:响应
2)请求的格式
Get请求:请求行 + 请求头

Post请求:请求行 + 请求头 + 请求体

常用的请求头:
- Accept: 表示客户端可以接收的数据类型
- Accpet-Languege: 表示客户端可以接收的语言类型
- User-Agent: 表示客户端浏览器的信息
- Host: 表示请求时的服务器ip 和端口号
哪些是get请求,哪些是post:
| GET请求 | POST请求 |
| :—————————————————————————————: | :——————————: |
| form 标签 method=get
a 标签
link 标签引入css
Script 标签引入js 文件
img 标签引入图片
iframe 引入html 页面
在浏览器地址栏中输入地址后敲回车 | form 标签 method=post |
3)响应的格式

- 响应行 + 响应头 + 响应体
常用的响应码:
- 200 表示请求成功
- 302 表示请求重定向
- 404 表示请求服务器已经收到了,但是你要的数据不存在(请求地址错误)
- 500 表示服务器已经收到请求,但是服务器内部错误(代码错误)
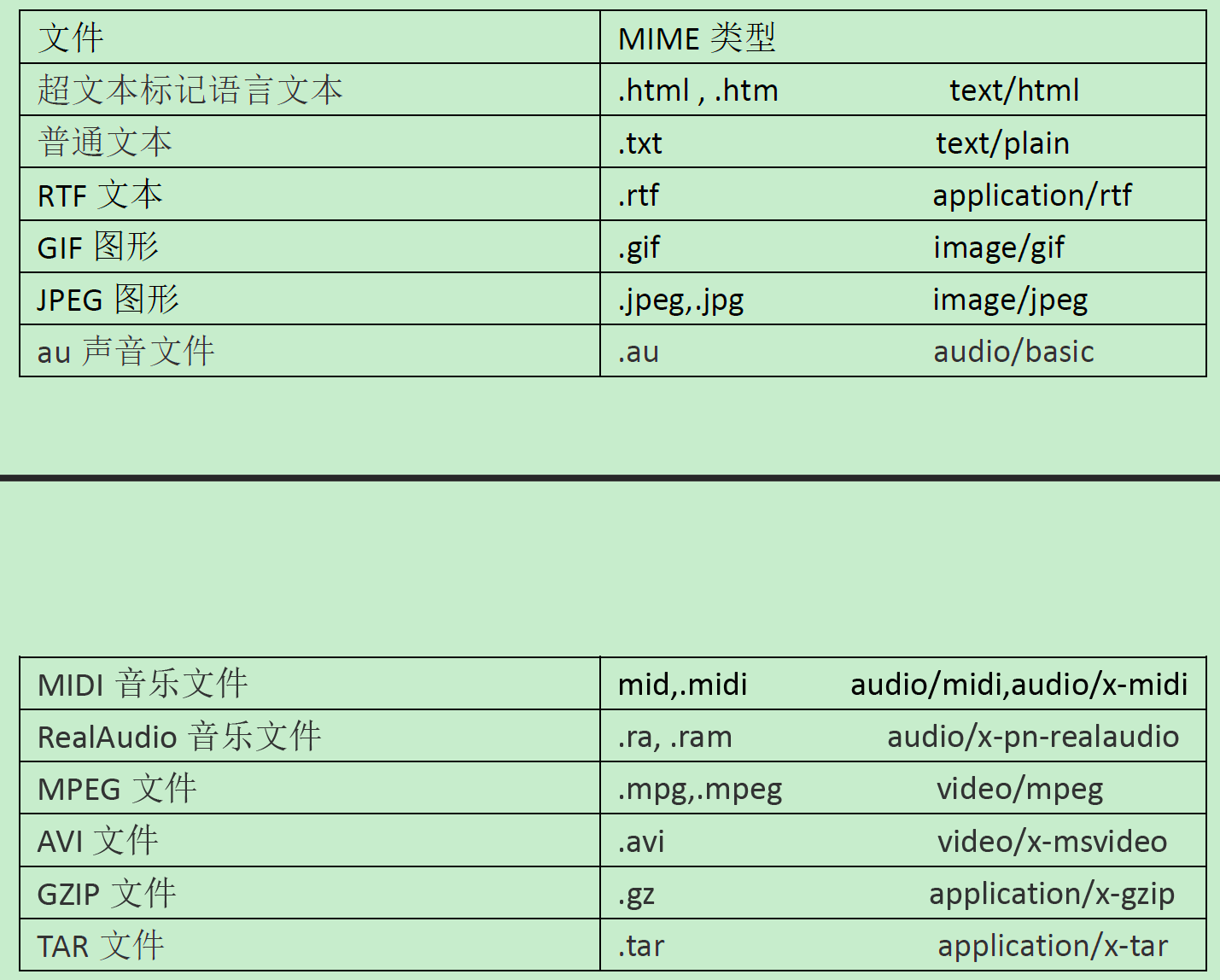
MIME 类型说明:
MIME 是HTTP协议中数据类型,”Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions” 多功能Internet邮件扩充服务。
MIME 类型的格式是“大类型/小类型”,并与某一种文件的扩展名相对应。
五、HttpServletRequest类
1)概述
每次只要有请求进入Tomcat服务器,Tomcat服务器就会把请求过来的HTTP协议信息解析好封装到Request对象中。然后传递到service方法(doGet 和doPost)中给我们使用。我们可以通过HttpServletRequest对象,获取到所有请求的信息。
2)HttpServletRequest类的常用方法
getRequestURI()获取请求的资源路径getRequestURL()获取请求的统一资源定位符(绝对路径)getRemoteHost()获取客户端的ip 地址getHeader()获取请求头getParameter()获取请求的参数getParameterValues()获取请求的参数(多个值的时候使用)getMethod()获取请求的方式GET 或POSTsetAttribute(key, value); 设置域数据getAttribute(key); 获取域数据getRequestDispatcher()获取请求转发对象
public class RequestAPIServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException {
// i.getRequestURI() 获取请求的资源路径
System.out.println("URI => " + req.getRequestURI());
// ii.getRequestURL() 获取请求的统一资源定位符(绝对路径)
System.out.println("URL => " + req.getRequestURL());
// iii.getRemoteHost() 获取客户端的ip 地址
/**
* 在IDEA 中,使用localhost 访问时,得到的客户端ip 地址是===>>> 127.0.0.1
* 在IDEA 中,使用127.0.0.1 访问时,得到的客户端ip 地址是===>>> 127.0.0.1
* 在IDEA 中,使用真实ip 访问时,得到的客户端ip 地址是===>>> 真实的客户端ip地址
*/
System.out.println("客户端ip 地址=> " + req.getRemoteHost());
// iv.getHeader() 获取请求头
System.out.println("请求头User-Agent ==>> " + req.getHeader("User-Agent"));
// vii.getMethod() 获取请求的方式GET 或POST
System.out.println( "请求的方式==>> " + req.getMethod() );
}
}3)获取请求参数
表单
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/07_servlet/parameterServlet" method="get">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br/>
兴趣爱好:<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="cpp">C++
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="java">Java
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="js">JavaScript<br/>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>java代码
public class ParameterServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException {
// 更改编码方式,以解决乱码关系,要在获取请求参数之前调用
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// 获取请求参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
String[] hobby = req.getParameterValues("hobby");
System.out.println("用户名:" + username);
System.out.println("密码:" + password);
System.out.println("兴趣爱好:" + Arrays.asList(hobby));
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException {
// 设置请求体的字符集为UTF-8,从而解决post请求的中文乱码问题
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
System.out.println("-------------doPost------------");
// 获取请求参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
String[] hobby = req.getParameterValues("hobby");
System.out.println("用户名:" + username);
System.out.println("密码:" + password);
System.out.println("兴趣爱好:" + Arrays.asList(hobby));
}
}
# doget请求中文乱码时,更改编码即可
// 获取请求参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
// 先以iso8859-1 进行编码,再以utf-8 进行解码
username = new String(username.getBytes("iso-8859-1"), "UTF-8");4)请求的转发
请求转发是指,服务器收到请求后,从一次资源跳转到另一个资源的操作叫请求转发。

public class Servlet1 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException {
// 获取请求的参数(办事的材料)查看
String username = req.getParameter("username");
System.out.println("在Servlet1(柜台1)中查看参数(材料):" + username);
// 给材料盖一个章,并传递到Servlet2(柜台2)去查看
req.setAttribute("key1","柜台1 的章");
// 问路:Servlet2(柜台2)怎么走
/**
* 请求转发必须要以斜杠打头,/ 斜杠表示地址为:http://ip:port/工程名/ , 映射到IDEA 代码的web 目录
*/
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("/servlet2");
// RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("http://www.baidu.com");
// 走向Sevlet2(柜台2)
requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
}
}
public class Servlet2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException {
// 获取请求的参数(办事的材料)查看
String username = req.getParameter("username");
System.out.println("在Servlet2(柜台2)中查看参数(材料):" + username);
// 查看柜台1 是否有盖章
Object key1 = req.getAttribute("key1");
System.out.println("柜台1 是否有章:" + key1);
// 处理自己的业务
System.out.println("Servlet2 处理自己的业务");
}
}5)base标签的作用

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh_CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- base标签设置页面相对路径工作时参照的地址,一旦设置了该值,浏览器中的地址值就会被忽略而采用该值 -->
<base href="http://localhost:8080/07_servlet/a/b/">
</head>
<body>
这是a下的b下的c.html页面<br/>
<a href="../../index.html">跳回首页</a><br/>
</body>
</html>6)web中斜杠的不同意义
在web中/斜杠是一种绝对路径。
- 斜杠如果被浏览器解析,得到的地址是:
http://ip:port/ - 斜杠如果被服务器解析,得到的地址是:
http://ip:port/工程路径- 1、
<url-pattern>/servlet1</url-pattern> - 2、
servletContext.getRealPath(“/”); - 3、
request.getRequestDispatcher(“/”);
- 1、
- 特殊情况: response.sendRedirect(“/”); 把斜杠发送给浏览器解析。得到
http://ip:port/
六、HttpServletResponse类
1)概述
2)两种输出流
- 字节流
getOutputStream():常用于下载(传递二进制数据) - 字符流
getWriter():常用于回传字符串(常用) - 两个流同时只能使用一个。使用了字节流,就不能再使用字符流,反之亦然,否则就会报错。
3)往客户端回传数据
public class ResponseIOServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException {
// 要求: 往客户端回传字符串数据。
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();
writer.write("response's content!!!");
}
}4)解决中文乱码
// 方法一(推荐)
// 它会同时设置服务器和客户端都使用UTF-8 字符集,还设置了响应头
// 此方法一定要在获取流对象之前调用才有效
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
// 设置服务器字符集为UTF-8
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// 通过响应头,设置浏览器也使用UTF-8 字符集
resp.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html; charset=UTF-8");5)请求重定向
请求重定向,是指客户端给服务器发请求,然后服务器告诉客户端说。我给你一些地址。你去新地址访问。叫请求重定向(因为之前的地址可能已经被废弃)。

// 请求重定向的第一种方案(推荐使用):
resp.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080");
// 请求重定向的第二种方案:
// 设置响应状态码302 ,表示重定向,(已搬迁)
resp.setStatus(302);
// 设置响应头,说明新的地址在哪里
resp.setHeader("Location", "http://localhost:8080");本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!